what is the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus Pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus (dm), type ii
Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a common metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels due to the body’s inability to properly use insulin or produce enough of it. This condition affects millions of individuals worldwide and has a significant impact on their overall health. Understanding the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes is crucial in managing the disease and preventing its complications. The pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes involves several key factors. One of the main contributors is insulin resistance, which occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate glucose levels in the blood. In individuals with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance prevents glucose from entering the cells, leading to an increase in blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance is often associated with obesity and is influenced by both genetic and lifestyle factors. Excess body weight, particularly in the abdominal area, can contribute to insulin resistance by promoting chronic inflammation and increasing the release of fatty acids and certain hormones. This creates a vicious cycle in which insulin resistance leads to weight gain, and weight gain exacerbates insulin resistance. In addition to insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion also plays a role in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. The pancreas produces insulin in response to elevated blood glucose levels, but in individuals with type 2 diabetes, the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin or release it efficiently. This impairment further contributes to the elevated blood sugar levels seen in this condition. Another important factor in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes is the dysfunction of the incretin system. Incretins are hormones released by the intestine in response to food intake, and they help regulate insulin secretion and glucose metabolism. In individuals with type 2 diabetes, there is a reduced response to incretins, leading to inadequate insulin release and impaired glucose metabolism. Furthermore, chronic inflammation and oxidative stress play a role in the development and progression of type 2 diabetes. Inflammation can impair insulin signaling pathways and promote insulin resistance, while oxidative stress can damage pancreatic beta cells, further impairing insulin secretion. These processes create a harmful cycle that perpetuates the pathophysiology of the disease. The pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes is complex and involves a combination of factors, including insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion, dysfunction of the incretin system, and chronic inflammation. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial in developing effective treatment strategies and preventing the complications associated with this condition. In conclusion, type 2 diabetes mellitus is a common and complex metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. The pathophysiology of this disease involves insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion, dysfunction of the incretin system, and chronic inflammation. These factors contribute to the development and progression of the disease and its associated complications. By gaining a better understanding of the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes, healthcare professionals can improve treatment approaches and help individuals manage their condition effectively.
If you are looking for Diabetes Mellitus: Nursing Care Management you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Pics about Diabetes Mellitus: Nursing Care Management like Diabetes Mellitus: Nursing Care Management, The Early Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes - The American Journal of Medicine and also Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus | Download Scientific Diagram. Here it is:
Diabetes Mellitus: Nursing Care Management
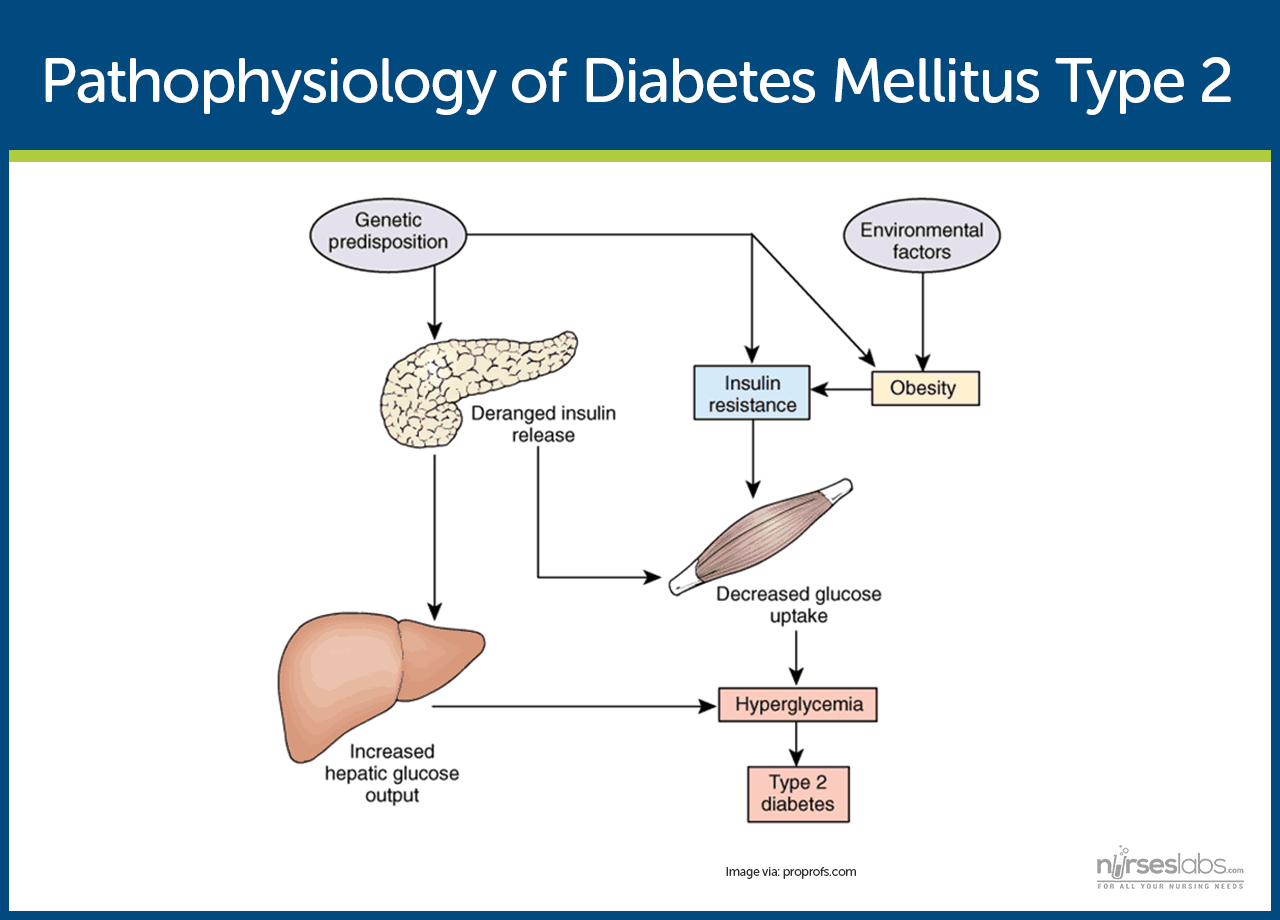 nurseslabs.comdiabetes mellitus pathophysiology nursing nurseslabs medika
nurseslabs.comdiabetes mellitus pathophysiology nursing nurseslabs medika
Pathophysiology | Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
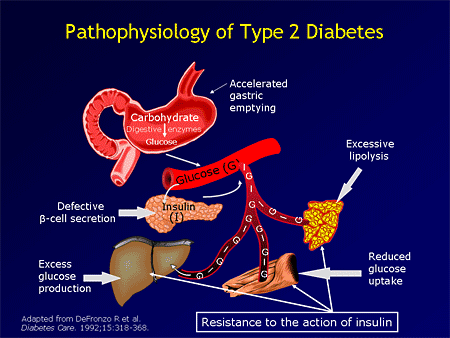 u.osu.edudiabetes type pre pathophysiology symptoms hypertension mellitus niddm easy medscape slide viewarticle gif diagnosis patient
u.osu.edudiabetes type pre pathophysiology symptoms hypertension mellitus niddm easy medscape slide viewarticle gif diagnosis patient
Pathogenesis Of Diabetes Mellitus (DM), Type II | Calgary Guide
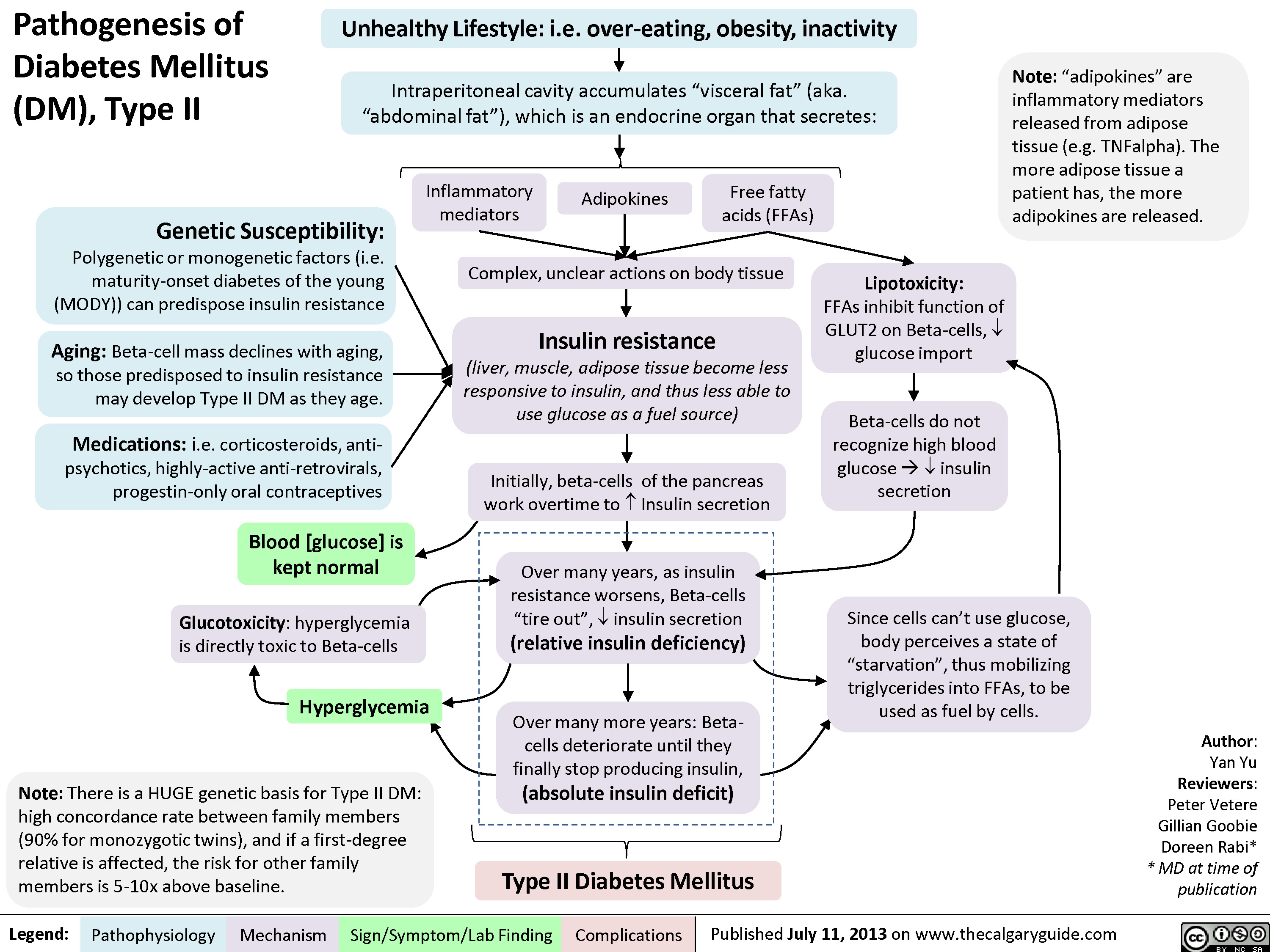 calgaryguide.ucalgary.cadm pathogenesis diabetes mellitus type ii calgaryguide calgary guide views post
calgaryguide.ucalgary.cadm pathogenesis diabetes mellitus type ii calgaryguide calgary guide views post
Pathophysiology Of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus | Download Scientific Diagram
 www.researchgate.netdiabetes pathophysiology mellitus type pathogenesis
www.researchgate.netdiabetes pathophysiology mellitus type pathogenesis
The Early Treatment Of Type 2 Diabetes - The American Journal Of Medicine
 www.amjmed.comtreatment pathophysiology insulin supplement
www.amjmed.comtreatment pathophysiology insulin supplement
Treatment pathophysiology insulin supplement. Dm pathogenesis diabetes mellitus type ii calgaryguide calgary guide views post. Diabetes type pre pathophysiology symptoms hypertension mellitus niddm easy medscape slide viewarticle gif diagnosis patient